|
"It's not that I'm so smart, it's just that I stay
with problems longer." - Albert Einstein
- Determine the maximum elongation in a 100-foot steel cable if the maximum
strain is 0.0035 and the allowable
tensile stress is 50,000 psi. Assume the modulus of elasticity of steel is E
= 29,000,000 psi.
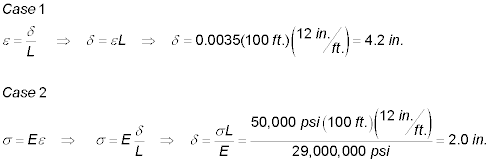
The controlling value for the area is that computed in Case 2 - the maximum
elongation to prevent failure in stress or strain is = 2.0 in.
- What is the average failure stress for 5 concrete specimens molded in
3 in. x 6 in. cylinders where the ultimate loads were 29,100 lb., 28,800
lb., 27,500 lb., 28,500 lb., and 28,800 lb., respectively?
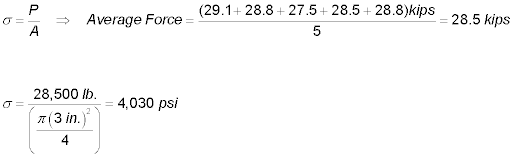
- If 3 cubic yards (yd.3) of
concrete are ordered for project, estimate the weight of cement, fine
aggregate, coarse aggregate and water required for a 1:2:3 mix with a w/c
= 0.35 (assume concrete weighs 150 lb./ft.3).

-
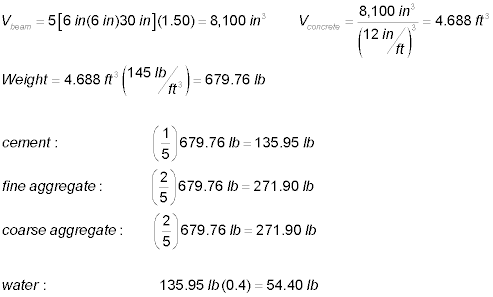
Determine the amount of cement, fine aggregate, coarse
aggregate and water required to
mix and construct five beams, each having the dimensions shown
in the figure below. Include a "make-sure-you-have-enough" factor of 1.5 in your mix calculations.
Assume a w/c ratio of 0.4 and a mix design of 1:2:2. Assume that
concrete weight 145 lb./ft3. All weights should be
reported in 0.05 lb. increments (just like in lab).

-
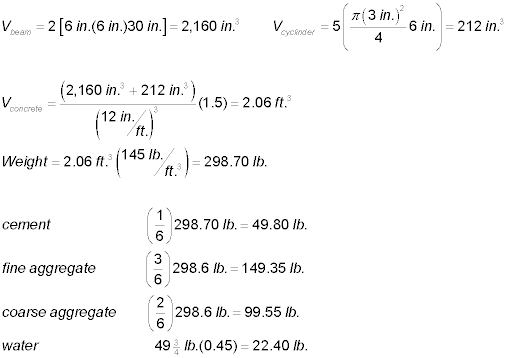
Rework Problem #4 to determine the amount of cement, fine aggregate,
coarse aggregate and water required to
mix and construct two beams, each having the dimensions shown in the figure
above, and five 3 in. x 6 in. cylinders. Include a
"make-sure-you-have-enough" factor of 1.5 in your mix calculations.
Assume a w/c ratio of 0.45 and a mix design of 1:3:2. Assume that
concrete weight 145 lb./ft3. All weights should be
reported in 0.05 lb. increments (just like in lab).
This website was originally
developed by
Charles Camp for
CIVL
1101.
This site is
Maintained by the
Department of Civil Engineering
at the University of Memphis.
Your comments and questions are welcomed.
|



