|
“A bargain ain't a bargain unless
it's something you need.” - Sidney Carroll
Repeat
GIS
Project #2,
however in this application, use the ArcGIS ArcToolbox command Analyst Tool
→ Proximity → Multiple Ring Buffer to generate 20
buffered areas at one mile intervals out to 20 miles from the construction site
and then use the command Analyst Tool
→ Overly → Identity to measure the distances from the
University of Memphis Construction site to each material vendor. Compare the
distances with those measured manually with ArcGIS Measure tool.
Use the
spreadsheet developed GIS Project
#2 to
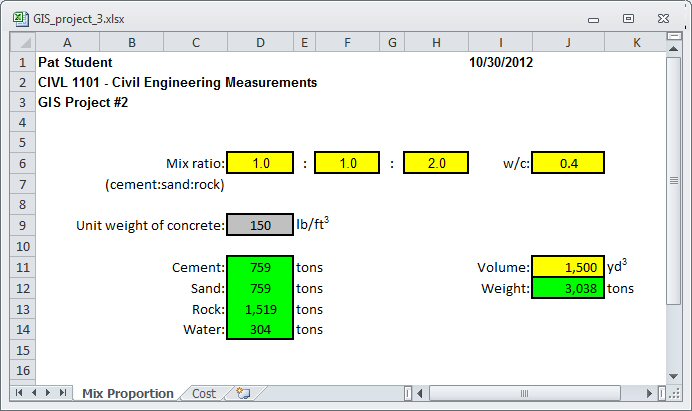
calculation of the total cost of delivered materials. Compute the total cost of delivered materials required to make
1,500 yd3 of concrete with a mix
ratio of 1:1:2 with a w/c ratio of 0.4 (assume that
concrete weight 150 lbs/ft3).
Next, use the ArcGIS concrete material database (Concrete_materials)
to estimate the distance from each material vendor to the Engineering Science
Building (the delivery point) and collect data for unit cost ($/ton/mile) and
inventory volume (tons) for each concrete material. With data for unit cost,
volume, and delivery distance for each material, estimate the minimum delivery
cost for the required concrete materials. The total cost of each delivered
material may be estimated as:
Total Cost ($) = Unit Cost ($/ton/mile) x
Volume (tons) x Distance (miles)
For convenience, vendors require the estimated
delivery distance to be rounded up to the next mile (for example, 5.24 miles is
6 miles). Also, note that if one vendor cannot supply all the material, several
vendors may be used. For simplicity, compute the minimum cost for each material
and then add the results together to estimate the minimum total cost.
Using ArcGIS, develop a map that shows the contour lines for
your site.
-
Open the ArcMap file you developed for GIS Project #2 that
contains the concrete materials and the construction site databases and save it
as GIS Project #3:
-
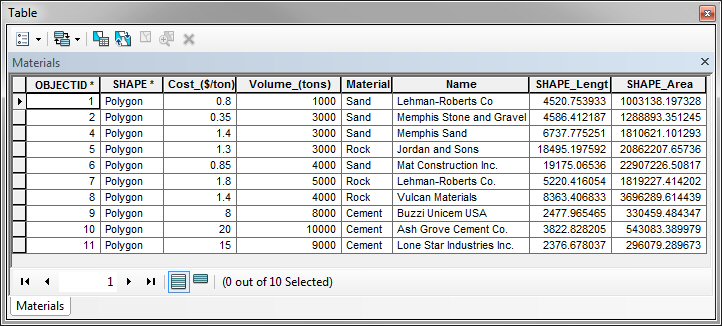
Review the attribute table for the Materials layer by
right-clicking on the Materials layer in the Table of
Contents and then click on Open Attribute Table.
-
Instead of manually measuring the distances between each
vendor and the University of Memphis (as we did in
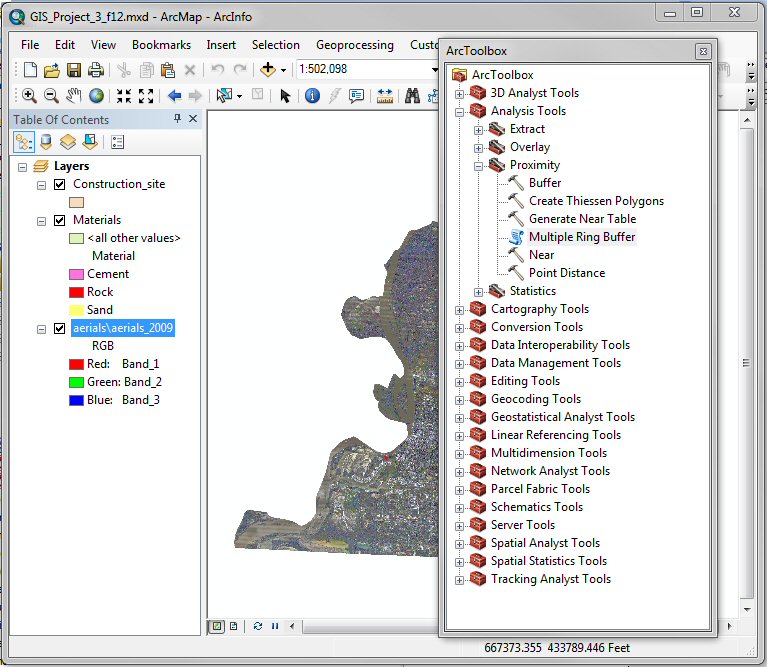
GIS Project #2), use the ArcGIS ArcToolbox command Analyst Tool
→ Proximity → Multiple Ring Buffer to
generate 20 buffered areas at one mile intervals out to 20 miles from the
construction site.
-
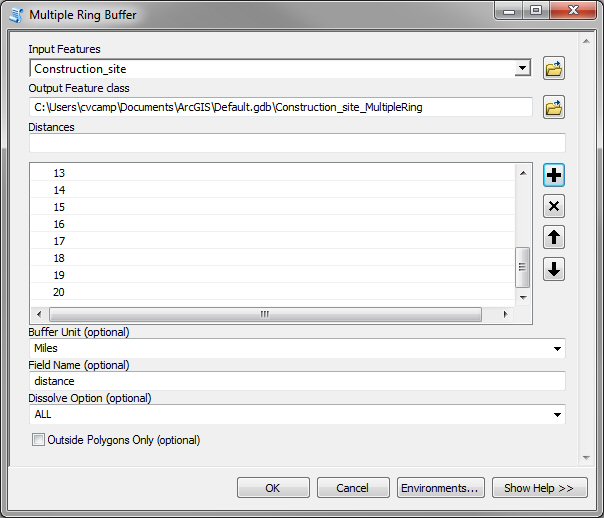
In the Multiple Ring Buffer window, shown below, make
the following entries:
-
Select Construction_site as the Input feature.
-
Take note of the name of the Output Feature class and
where it will be located: Default.gdb\Construction_site_MultipleRing
-
Change the Buffer Unit to miles by using the pull-down
menu on the right side of the input line.
-
Manually enter the distance of each buffer on the
Distances input line and then click the
 button.
button.
-
Repeat this process and enter the distances 1 through 20
miles.
-
This computation can take a few minutes. While ArcGIS is
working, a banner will appear along the bottom edge of the window and run
while the computation is active.
-
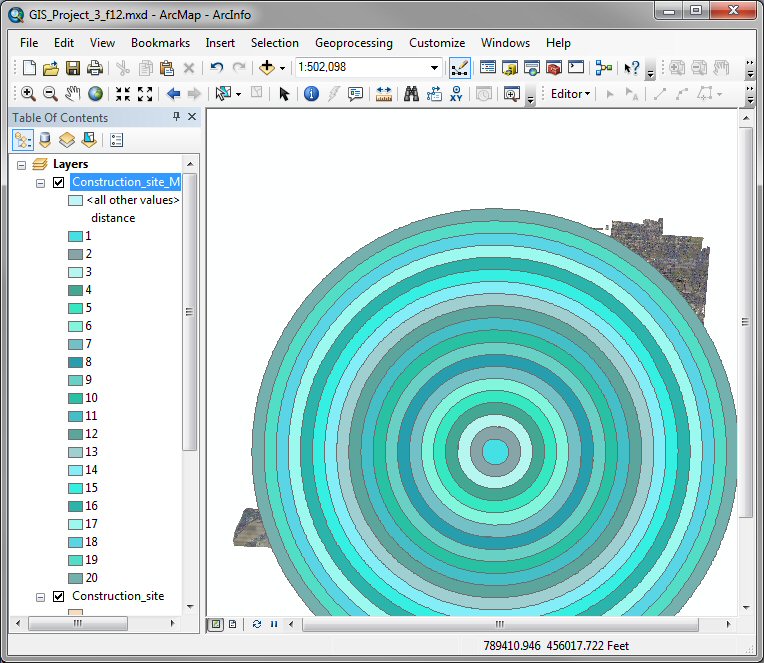
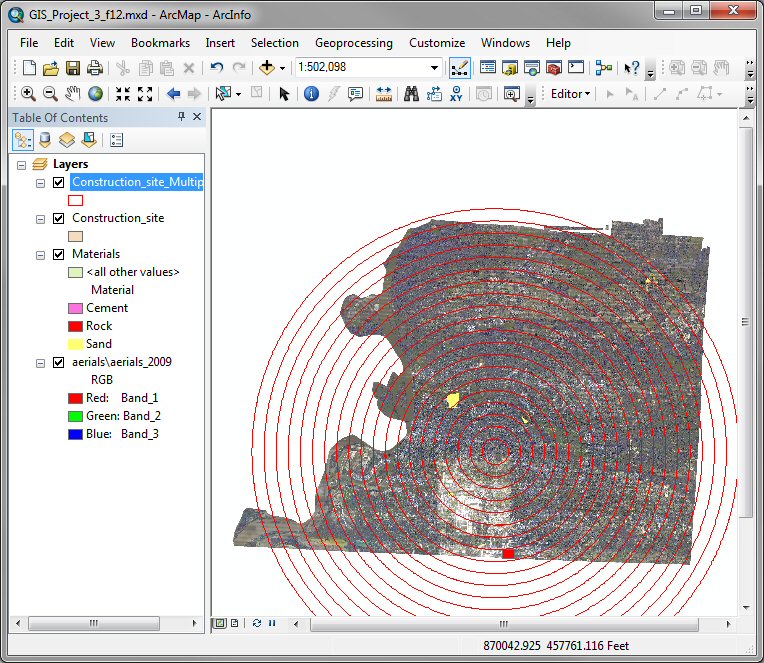
After the Multiple Ring Buffer has finished you
should see a series of rings around the construction site at 1 mile
intervals.
-
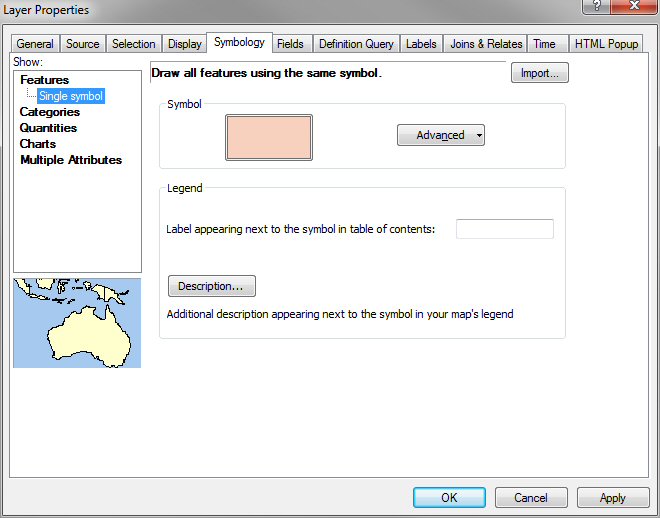
Double click on the Construction_site_MultipleRing
layer and select the Symbology tab of the Layer Properties
window and select Features in the Show menu on the right side
of the window.
-
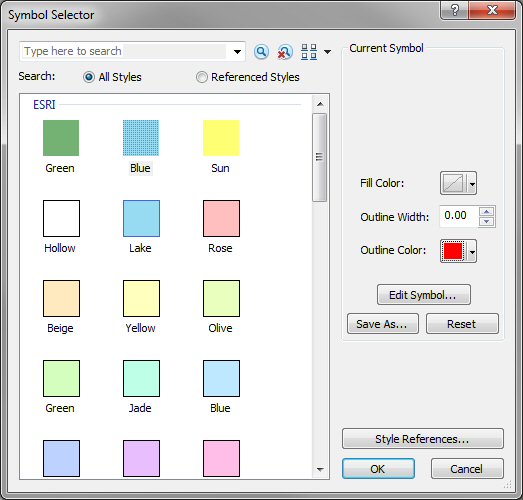
Click on the Symbol color box and change the Fill Color
and Outline Color values on the Symbol Selector window. Probably a
bright outline color and no fill color would be best.
-
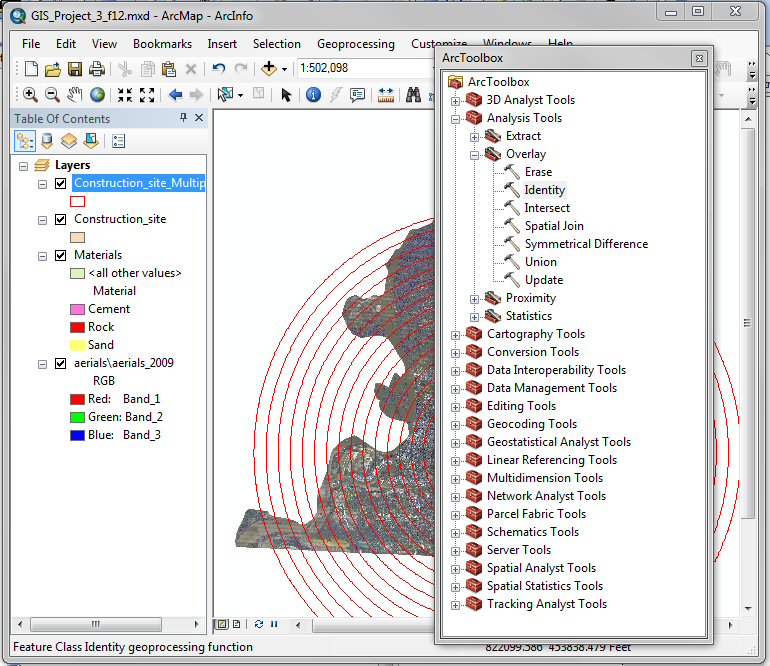
Use the command Analyst Tool
→ Overly → Identity to measure the distances
from the University of Memphis Construction site to each material vendor.
-
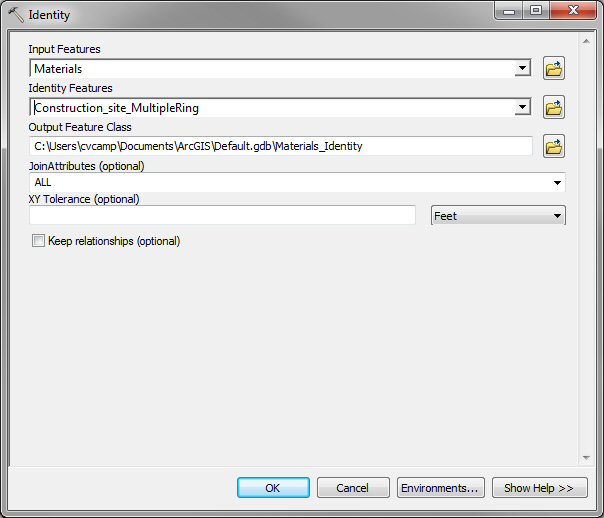
In the Identity window choose the Materials
layer as the Input Feature and the Construction_site_MultipleRing
buffer as the Identity Features and click OK. Note the name
and location of the Output Feature Class: Default.gdb\Materials_Identity
-
After Identity runs, a new layer is added to your
map: Materials_Identity. Right-click on the Materials_Identity layer in the Table of
Contents and click on Open Attribute Table. You should notice that there
are additional data in the table, in particular a new field called
Distance.
-
Export this database to an Excel file by clicking on the
Table Options (top-right button on the Table window) and then on
Export.
-
Update your distance measurements in the
GIS Project #2 Excel spreadsheet.
If a vendor has multiple entries in the Distance field of the
Materials_Identity table, use the large of the two values.
- Using the following equation: Total Cost ($) =
Unit Cost ($/ton/mile) x
Volume (tons) x Distance (miles) compute the cost for each vendor to
deliver material.
- Use your spreadsheet to estimate the minimum cost to supply the required
materials for 1,500 yd3 of
concrete.
-
Print out the coversheet
and a copy of your spreadsheet.
Print
coversheet for homework
This website was originally
developed by
Charles Camp for
CIVL
1101.
This site is
Maintained by the
Department of Civil Engineering
at the University of Memphis.
Your comments and questions are welcomed.
|



