|
The following is a step-by-step procedure for analysis a two-dimensional truss
structure using SAP2000. The order of some of these steps is not critical; however,
all step should be completed before execution of the the analysis. If you have any
questions, or you you find any of these instructions unclear or inaccurate, please contact
Dr. Charles Camp.
To help students become familiar with some of the numerous aspects and features of SAP2000, the following tutorial will focus on determining the forces in each member of the
roof truss shown below. Assume all
members are pin connected.
When you start SAP2000 Educational Version
11.0.7 you should see the
following interface window:
Step
1: Define Problem - Under the File
Menu, click on New Model.

The following New Model menu will appear as:
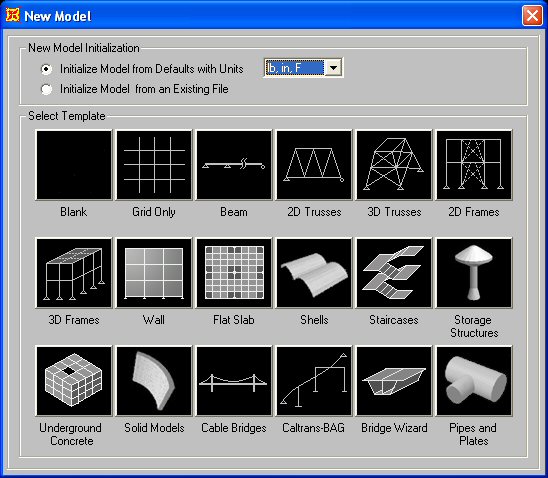
At the top of the New Model menu, select the
appropriate units for the analysis. In this example, the units are
inches
and kips.
In this
example we will used the Grid Only
option to build out truss model.
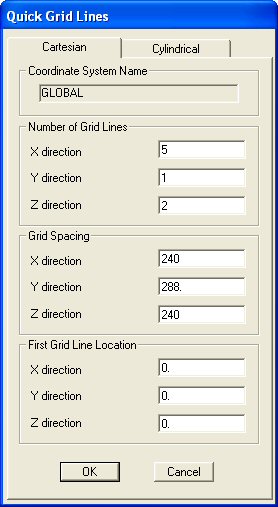
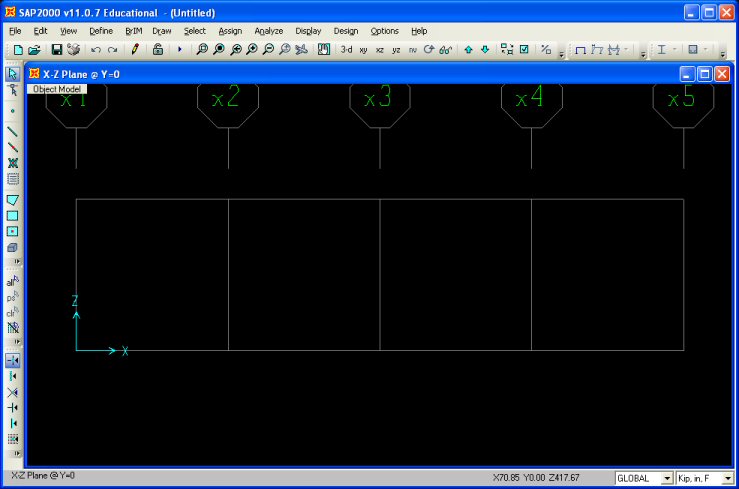
Step 2: Grid Spacing - Determine the appropriate number of
grid lines and grid spacing to locate the joints of the truss. The grid spacing is set by
defining a new problem.
| When
you select Grid Only on the New Model menu, the
Quick Grid Lines
window will appear (see the figure on the right).
Remember,
that SAP2000 assumes that your two-dimensional structure resides in the x-z plane.
Define
your grid system by entering data on the Quick Grid Lines
window.
For the truss shown above, the the grid spacing in the
x and z-directions is 240 inches. The number of grid lines in the x and z-directions are
5 and 2, respectively. While we do not need any
y-direction grid lines you must have at least one line.
When you click OK, SAP2000 generates the grids lines you have just
defined and shows you the grid system in the SAP2000 interface window.
By default SAP2000 show two views of your problem, typically a 3-D view and an x-y
plane view. |
 |
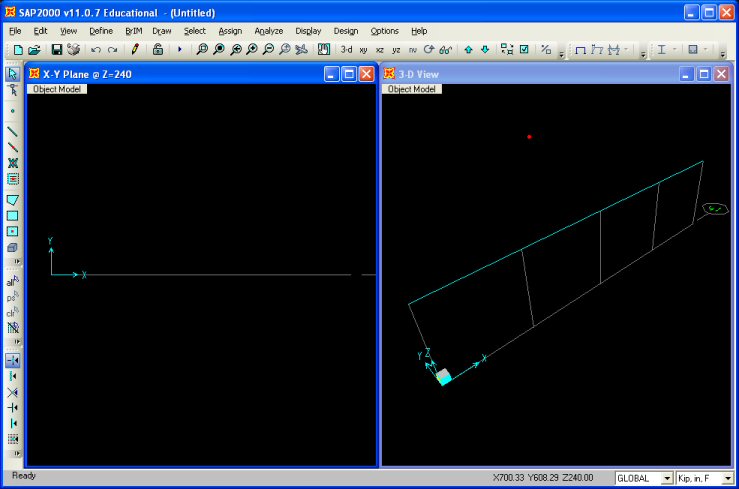
To adjust the views, select an window and click on the
appropriate view button located along the top edge of the interface window.
This analysis is in the x-z plane, so delete one of Object Model windows and
change view the remaining one to the xz plane by clicking
 in the row
of buttons along the top edge of the Object Model window. in the row
of buttons along the top edge of the Object Model window.
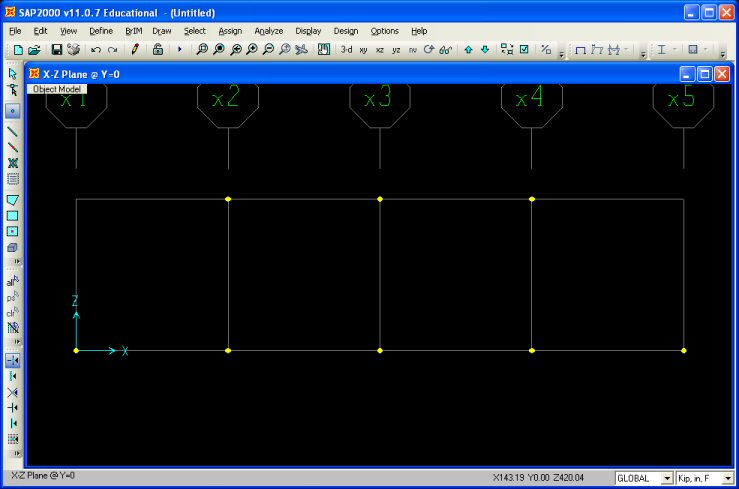
Step 3: Locate Truss Joints - To define the joint
locations, select the Draw Special Joint button  on the
left-hand side top bar on the main SAP200 interface. The Properties of Object
Window will appear, just close it and begin clicking on grid intersection lines to define joints. For this problem the
joint locations are shown below: on the
left-hand side top bar on the main SAP200 interface. The Properties of Object
Window will appear, just close it and begin clicking on grid intersection lines to define joints. For this problem the
joint locations are shown below:
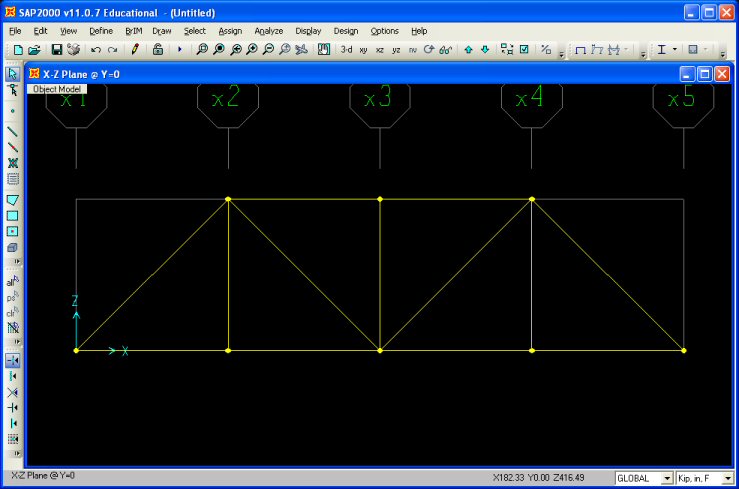
Step 4: Draw Frame Elements - To define each
frame element, select the Draw Frame Element button
 on the
left-hand side top bar on the main SAP200 interface. The Properties of Object
Window will appear, just close it. on the
left-hand side top bar on the main SAP200 interface. The Properties of Object
Window will appear, just close it.
To define an element, click on a joint at the beginning of the element
and than on the joint at the end of the element. To end a series of element definitions,
simply double-click on the final joint. For this truss problem, the frame elements are
shown below:
Step 5: Define Structural Supports - To define
the location and type of structural support, select the support location by clicking on
the joint with the pointer. A yellow "X" should appear at the joint to indicate
that it is currently selected. Next click on the Assign menu, then
on Joint, then Restraints.
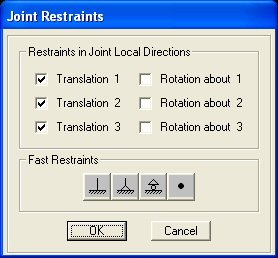
| The Joint
Restraints menu will appear as shown on the right. In most cases, the directions 1,
2, and 3 listed on the menu correspond to the x, y, and
z directions. When working on two-dimensional structures, the Fast Restraints
button may be used for most problems. If the support conditions for your problem are not
listed in the Fast Restraints section of the menu, you should select the
appropriate combination of restraints. In the
truss example, select the lower-left hand joint with the pointer (an "X"
should appear at the joint). On the Fast Restraints menu select the pin
button  and click OK.
and click OK.
Next, select the lower right-hand joint with the pointer
and on the Fast Restraints menu select the roller
button
 and click OK. and click OK. |
 |
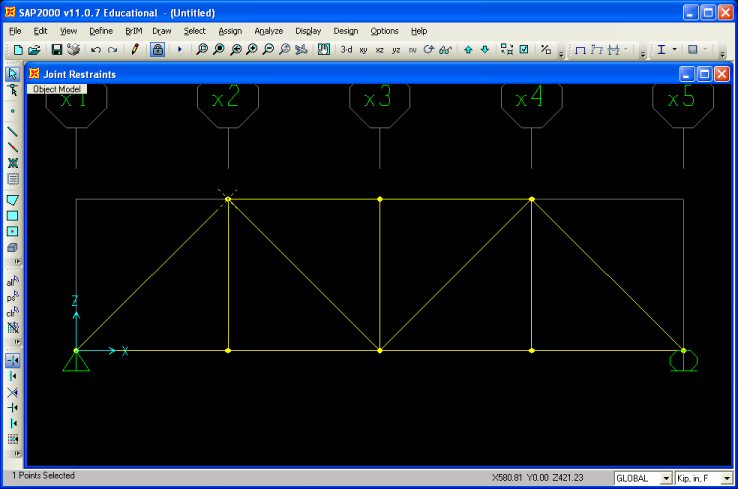
After the supports have been defined the truss problem should appear in the SAP2000
interface window as follows:
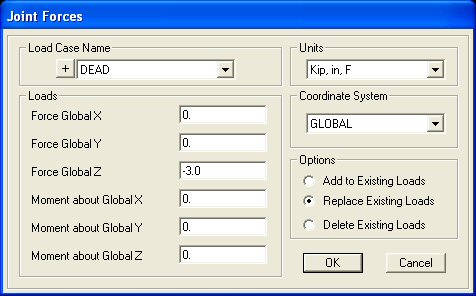
Step 6: Apply Forces at Joints - To apply forces at a
joint, select the joint with the pointer and click on the Assign =>
Joint Loads => Forces. The following menu will appear:
| In this
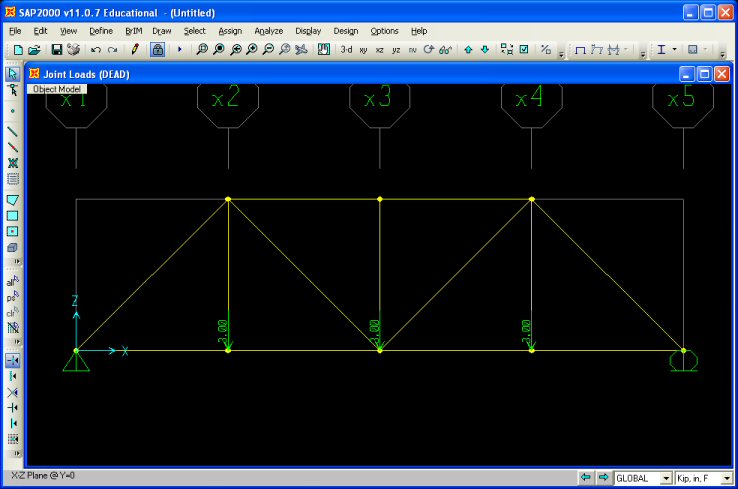
example, there are three 3 kip forces acting along the bottom cord of the truss. Remember
that the truss was modeled in the in the x-z plane, therefore the forces are acting in the
negative z-direction. Enter -3.0 in the Forces Global Z input field and
click OK. The forces should be should be displayed on the truss (proper
direction and magnitude) in the SAP2000 interface window. |
 |
Step 7: Release Internal Moments at Joints - SAP2000
assumes that all structures are frames. Therefore, to analyze a truss structure we should
convert each joint from a fixed connection to a pin connection. To ensure that every joint
in the structure is pin connected, select all the members by clicking the Select
All button on the left tool bar. Next click on Assign menu and
select Frame then Releases and the and Frame
Releases window will appear.
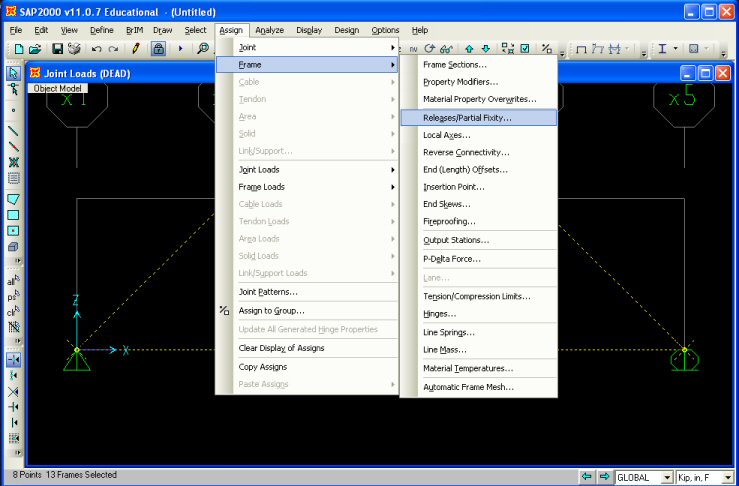
| In this
example, the structure is a truss, which by definition has no moment capacity at each joint.
To release the moment capacity, click on the check boxes that are associated with the Moment
22, Moment 33, and Torsion.
Torsion can only be released at one end of the element, whereas, the other
moment must be released at both the
Start and End of the element.
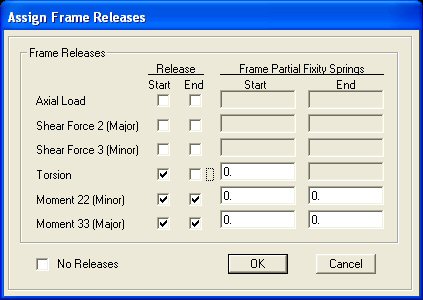
After the moments are released, the truss structure should appear in the SAP2000
interface window as follows: |
 |
Step 8: Define Material Properties - SAP2000 assumes the
loads acting on a structure include the weight of each weight. In our truss analysis, we
assume that each element is weightless. To define the properties of a material , select
the Define menu located along the top the SAP2000 interface window and
then click on Materials. The Define Materials window will appear as shown
below:
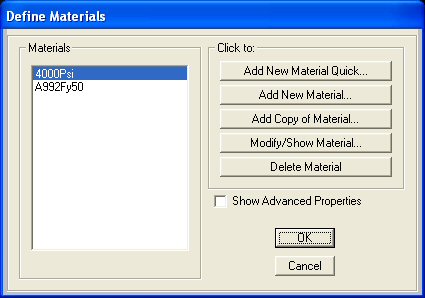 |
On this menu
you can change the properties of materials. In this example, select the
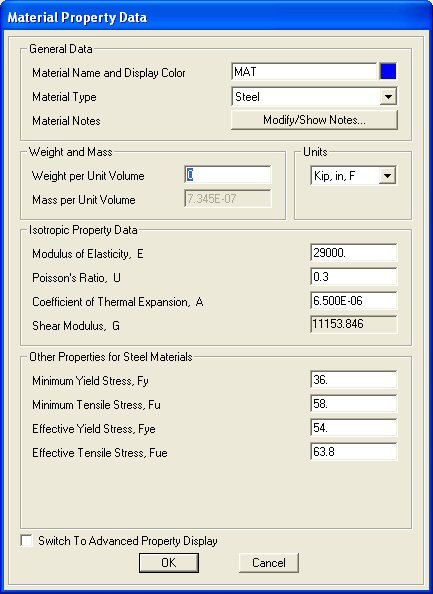
Add New Material button and the Material Property Data window will appear. |
Change the
value in the Weight per unit Volume input field to zero. Click OK to return to the Define Materials window and
than click OK again. Now we have a material named MAT that has no weight per volume.
For this example problem, the default values for the Mass per unit Volume,
Modulus of Elasticity, Poisson's ratio, and the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion can
be used. For most linear-elastic statically loaded structures only values for
Weight per unit Volume and Modulus of elasticity are required.
Step 9: Define Frame Sections - To define the cross-section
properties of a structural element click on the Define menu located along
the top the SAP2000 interface window and then click on Frame Sections.
The Define Frame Sections window will appear as shown below:
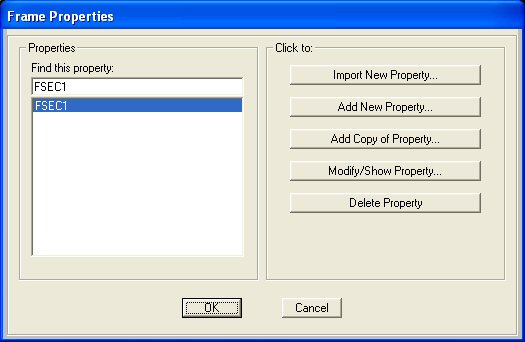
The default
Frame Section label is FSEC1. To change the properties of the frame
section click on the on the Modify/Show Material button.
The I/Wide Flange Section window will appear.
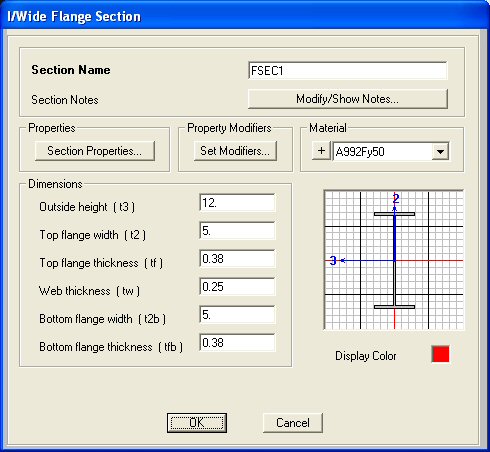
To the material
of this frame section click on the Material pull-down menu and select our
weightless material MAT. Click OK to return to the
I/Wide Flange Sections
window and than click OK again on the Frame Properties
window.
If you are interested in
computing deflections in the truss, then you must define the geometric
properties of the cross-section. In this example, we are interested only in the
axial forces in a determinate truss, so the value of the cross-sectional areas
are not important.
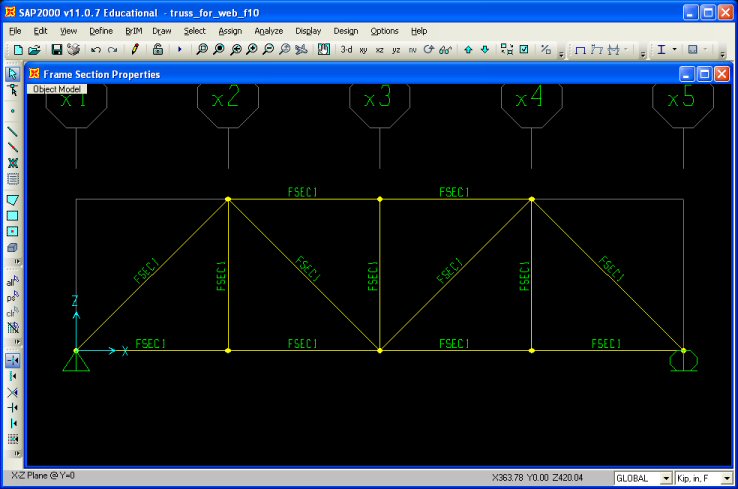
Step 10: Assign Frame Sections - To assign the
cross-section properties of a structural element, select the elements with the pointer and
click on the Assign menu located along the top the SAP2000 interface
window and then click on Frame Sections. You can assign the same section
properties multiple elements by selecting all the elements that share the same properties.
The Frame Section name will appear next to each element selected. After the frame sections
have been assigned the SAP2000 interface window will appear as follows:
Step 11: Set Analysis Options
and Run Analysis - In
this example, the truss structure is modeled in the x-z plane. To limit analysis to
variables in the x-z plane click on the Analyze menu located along the
top the SAP2000 interface window and then click on Set Analysis Options. The Analysis
Options menu will appear as follows:
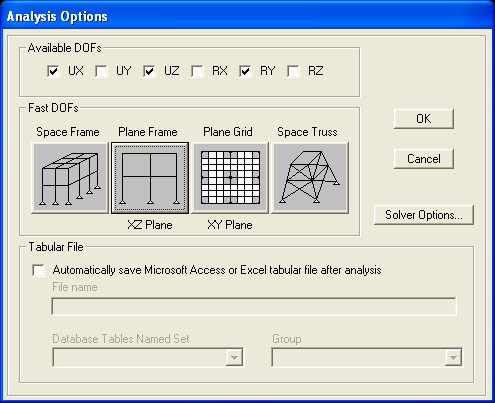
To restrict SAP2000 to variables in the x- plane, select the Plane Frame button and
click OK. The truss structure is now ready for analysis. To analyze the model press the Run
Analysis button
 .
The Set Analysis Cases to Run Menu will appear as below: .
The Set Analysis Cases to Run Menu will appear as below:
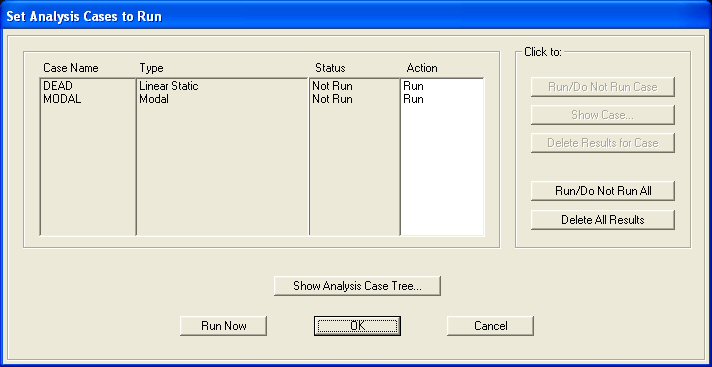
In SAP2000 is it possible to run many different types
of analyses
If the analysis is successful, the Analysis Complete window will
appear and report the the analysis is complete. Click OK and the
SAP2000 interface window will display an exaggerated deflected shape of the modeled
structure.
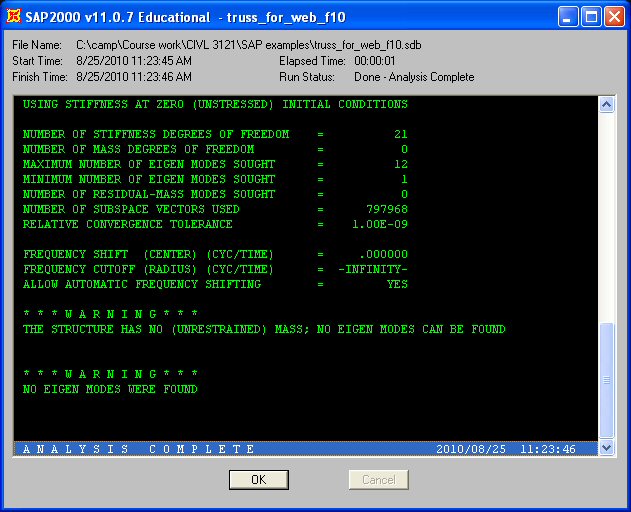
If the window reports that the analysis is incomplete, make sure that the moments have
been released and that the analysis options have been set correctly.
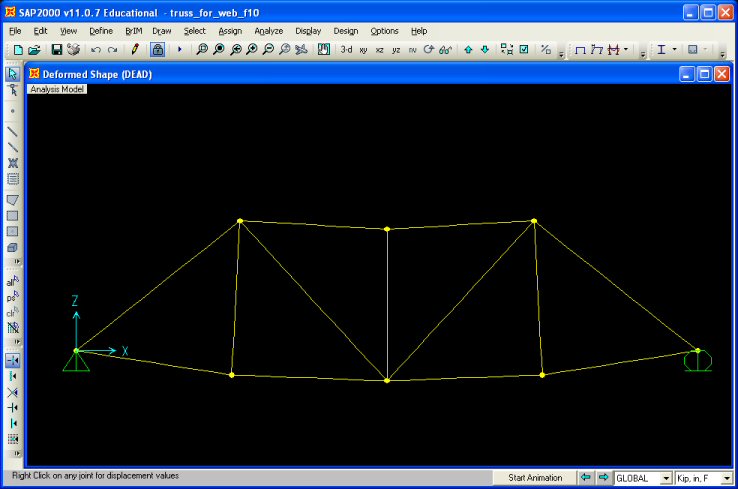
After
the Analysis Complete window has been closed, typically SAP2000 displays the deflected shape of the structure as shown below:
Step 12: Print Truss Forces - To get a quick feel for the
relative magnitude of the forces in the truss, select the Show Forces/Stresses button
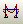 along the top tool bar. The Member
Force Diagram for Frame menu will appear as follows: along the top tool bar. The Member
Force Diagram for Frame menu will appear as follows:
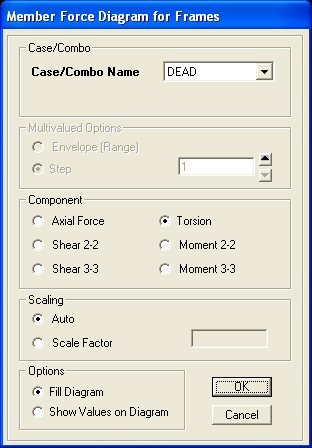 |
Click on the Axial Force using the Fill Diagram. If
you click OK, the SAP2000 interface window will display the relative magnitude of the
axial forces with compress forces in red and tension forces
in yellow.
Another way to display force information is to unclick Fill Diagram
and click on Show Values on Diagram. In this case, the value of each
axial force will be displayed next to the member (see the figure below). |
To print the results to a file click on the File menu and select Print
Tables and click the Print to File box. The following Choose Tables for
Printing window will appear.
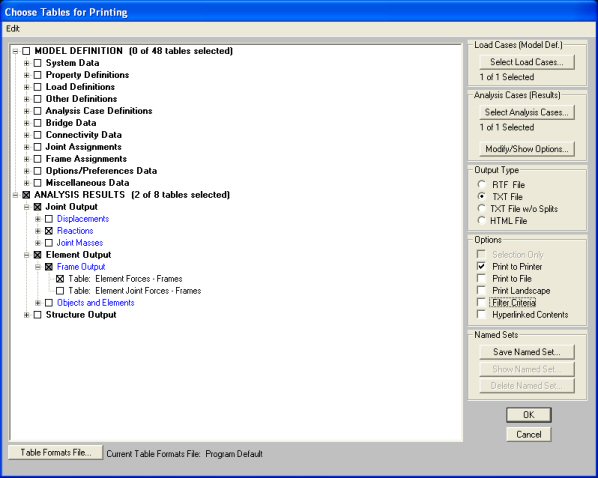
Select under Joint Output => Reactions and under
Element Output => Frame Output. Click on the Print to File option and
click OK. Choose a location and a filename and print the file
In order to correlation the results printed in the output file to frame elements
in the structure, the frame labels turned on and printed out. To display the
frame element labels click on the Show Undeformed Shape button
 on the
main interface. Next, click on the Set Display Options button on the
main interface. Next, click on the Set Display Options button
 and under
the Frames/Cables/Tendons section of the menu click on Labels. and under
the Frames/Cables/Tendons section of the menu click on Labels.
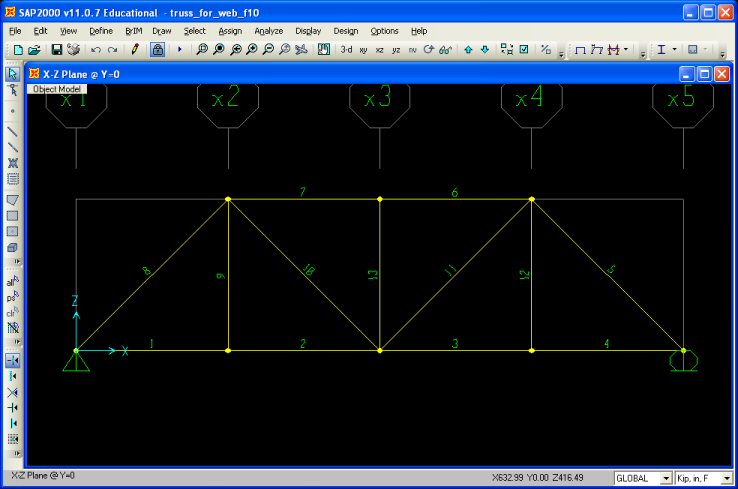
The frame element numbers, or any other information displayed in the main
SAP2000 interface, can be printed by clicking on the File menu and
selecting Print Graphics (the image will be sent to the default printer).
The results of the truss analysis presented in the output file are listed by
frame element number.
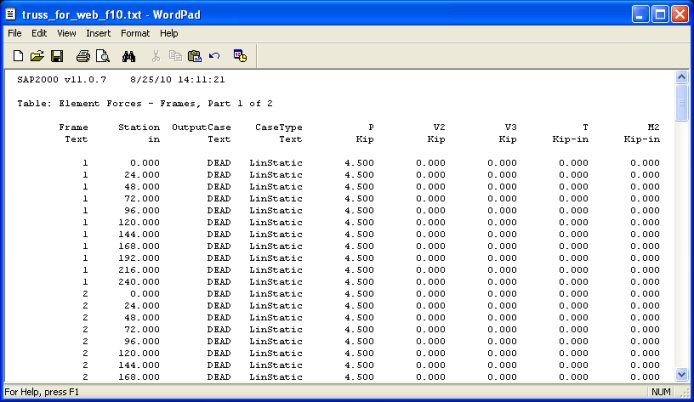
Note that SAP2000 list the variation of the internal forces and moments along
the element. For truss analysis there are no bending moments and shear forces.
The values listed in the "P" column are the axial forces in the truss members.
|



