![]()
Remarks
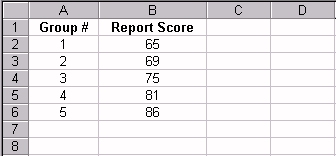
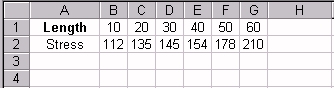
Cell C2 formula: MATCH(50, B1:G1, 0) results in 5 or the value
"50" is in the fifth column of the range B1:G1
![]()
MATCH returns the position of the matched value within lookup_array, not the value
itself. For example, MATCH("b",{"a","b","c"},0)
returns 2, the relative position of "b" within the array
{"a","b","c"}.
![]()
MATCH does not distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters when matching text
values.
![]()
If MATCH is unsuccessful in finding a match, it returns the #N/A error value.
![]()
If match_type is 0 and lookup_value is text, lookup_value can contain the wildcard
characters, asterisk (*) and question mark (?). An asterisk matches any sequence of
characters; a question mark matches any single character.
![]() Examples:
Examples: