CIVL 1101 - Assignment #4
Out of clutter, find simplicity.
From discord, find harmony.
In the middle of difficulty, lies opportunity -
Albert Einstein, The Three Rules of Work
Part 1: Consider the linear-elastic prismatic bar fixed on the left-hand-side and loaded by axial forces P at the right-hand-side, as shown in figure below (assume all measurements are "exact"). In all cases, report answers to three significant figures.
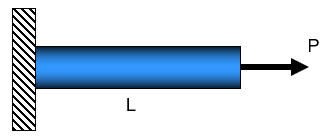
- If the allowable stress at failure for the material is
25,000 psi and the applied load on the bar is P = 15,000 lb., what is the
minimum area require to prevent failure?
- If the bar fails at strains greater than 0.050 and the
original length of the bar is L = is 24 in., what is the maximum
allowable deformation before failure?
- If the material in the bar is considered linear-elastic
and the tensile stress is 25,000 psi and the tensile strain is 0.020, what is the modulus
of elasticity of the material?
- If the original length of the bar is L =
10 ft. and it deforms 0.15 in., what is the stress in the material if the modulus of
elasticity of 29,000 ksi?
- Determine the cross-sectional area of a steel cable required to support a 15,000 lb. tensile force over 100 ft. while not exceed the an allowable tensile stress of 45,000 psi or a maximum elongation of 0.10 ft. Assume the modulus of elasticity of steel is E = 29,000,000 psi.
Part 2. Read Chapter 2 in the Strategies for Creative Problem Solving by Fogler and LeBlanc.